Technology has transformed how we live, work, and connect, making everyday tasks easier and more efficient. However, by 2025, concerns about tech addiction—the compulsive overuse of digital devices and services—are growing. What starts as convenience can evolve into dependency, impacting mental health, productivity, and social relationships.
So, when does helpful technology cross the line into harmful addiction? Let’s explore the causes, effects, and ways to find balance in our tech-driven lives.
1. What Is Tech Addiction?
Tech addiction refers to excessive or uncontrollable use of digital devices and platforms, such as smartphones, social media, video games, and streaming services. It’s characterized by:
- Cravings or urges to use technology.
- Difficulty limiting screen time.
- Negative impact on daily life and well-being.
- Withdrawal symptoms when not using devices.
This behavioral addiction affects people of all ages, with increasing prevalence worldwide.
2. Why Does Tech Addiction Happen?
Several factors drive tech addiction:
- Instant gratification from notifications, likes, and messages triggers dopamine release, reinforcing usage.
- Social validation encourages constant engagement with social media.
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) pushes users to stay connected.
- Design elements like infinite scrolling and autoplay videos exploit psychological vulnerabilities.
- Work demands and remote environments blur boundaries between personal and professional use.
Technology is designed to capture and hold our attention.
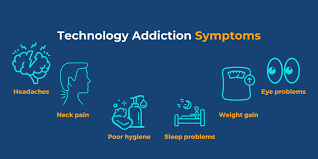
3. Effects of Tech Addiction
Tech addiction can lead to:
- Mental health issues like anxiety, depression, and stress.
- Sleep disturbances due to screen exposure before bedtime.
- Reduced productivity and focus problems.
- Social isolation as online time replaces face-to-face interaction.
- Physical health problems such as eye strain and sedentary lifestyle.
These consequences highlight the importance of managing tech use.
4. Recognizing the Signs
Common signs of tech addiction include:
- Feeling anxious or restless when not using devices.
- Neglecting responsibilities or relationships due to screen time.
- Using technology to escape negative emotions.
- Unsuccessful attempts to cut back on usage.
- Experiencing conflicts over device use.
Early awareness helps prevent deeper dependency.
5. Strategies to Overcome Tech Addiction
Balancing tech use requires intentional habits:
- Set screen time limits and use built-in monitoring tools.
- Schedule tech-free periods during the day.
- Turn off non-essential notifications to reduce distractions.
- Engage in offline activities like exercise, reading, or hobbies.
- Practice mindfulness and digital detoxes to reconnect with the present moment.
- Seek professional help if addiction significantly impairs life.
Building healthy tech habits improves well-being.
6. The Role of Tech Companies and Society
Technology creators and policymakers have responsibilities to:
- Design products that promote healthy usage, not dependency.
- Provide tools for users to control and monitor their habits.
- Educate the public about risks and responsible use.
- Encourage digital well-being as a priority.
A collaborative approach supports balanced tech ecosystems.
Final Thoughts
Technology offers incredible convenience and connection—but unchecked use can lead to addiction with serious consequences. Recognizing when convenience becomes dependency empowers us to reclaim control and foster healthier relationships with our devices.
By adopting mindful habits, setting boundaries, and promoting responsible design, we can enjoy the benefits of technology without sacrificing our mental and physical health.