3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is reshaping how products are designed, manufactured, and delivered. By 2025, this innovative technology is no longer limited to prototypes or small-scale projects; it is driving breakthroughs across industries—from healthcare and aerospace to fashion and construction.
With the ability to build complex objects layer by layer, 3D printing offers unprecedented flexibility, customization, and efficiency. Let’s explore how 3D printing is building the future and transforming manufacturing as we know it.
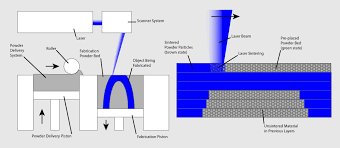
1. How 3D Printing Works
3D printing creates physical objects by depositing material layer upon layer, following a digital design file. Unlike traditional subtractive methods (cutting or molding), additive manufacturing:
- Minimizes waste by using only necessary material.
- Allows complex geometries impossible with conventional techniques.
- Enables rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
Materials range from plastics and metals to ceramics and even living cells.
2. Transforming Industries
- Healthcare: Custom prosthetics, dental implants, and even bioprinted tissues are improving patient outcomes.
- Aerospace: Lightweight, strong components reduce fuel consumption and manufacturing costs.
- Automotive: Rapid prototyping and production of specialized parts accelerate design cycles.
- Construction: 3D-printed houses and building components offer faster, sustainable solutions.
- Fashion and Art: Designers craft intricate, personalized pieces that push creative boundaries.
3D printing enables innovation previously constrained by manufacturing limits.
3. Benefits of 3D Printing
- Customization: Tailored products to fit individual needs or preferences.
- Speed: Faster production cycles from design to finished product.
- Cost-efficiency: Lower costs for prototyping and small-scale manufacturing.
- Sustainability: Reduced material waste and potential for recyclable materials.
- Supply Chain Simplification: On-demand production reduces inventory and shipping.
These advantages make 3D printing an attractive solution for many sectors.
4. Challenges to Overcome
Despite its promise, 3D printing faces challenges:
- Material limitations: Not all materials are printable or meet strength standards.
- Quality control: Ensuring consistent product reliability can be difficult.
- Speed for mass production: Scaling up to high-volume manufacturing remains a hurdle.
- Intellectual property concerns: Easy replication raises legal questions.
- Regulatory compliance: Especially in healthcare and aerospace, stringent standards apply.
Ongoing research and innovation aim to address these issues.
5. The Future Outlook
The future of 3D printing includes:
- Integration with AI and robotics for fully automated production.
- Development of new printable materials with enhanced properties.
- Expansion into new fields like food printing and biofabrication.
- More accessible, affordable 3D printers for consumers and small businesses.
3D printing will continue to blur the lines between design and manufacturing.
Final Thoughts
3D printing is revolutionizing manufacturing by offering unmatched design freedom, customization, and efficiency. As technology advances, its impact will grow—building the future layer by layer, one innovation at a time.
Whether in hospitals, factories, or homes, 3D printing is poised to redefine how we create and consume products.
